EpiNext™ 5-mC RNA Bisulfite-Seq Easy Kit (Illumina)
For streamlined RNA bisulfite conversion and NGS library preparation for 5-methylcytosine RNA-seq
Product Description
The EpiNext™ 5-mC RNA Bisulfite-Seq Easy Kit (Illumina) is a complete set of optimized reagents designed for easily carrying out RNA bisulfite conversion, followed by a "post-bisulfite" library preparation process for Illumina platform-based bisulfite sequencing, all in one kit.
Intended applications include whole transcriptome RNA bisulfite sequencing and various other RNA bisulfite-based next generation sequencing techniques for 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) based RNA methylation analysis.
The optimized protocol and components of the kit allow the RNA to be bisulfite converted and fragmented simultaneously, followed by quick non-barcoded (singleplexed) and barcoded (multiplexed) library construction using low-nanogram quantities of bisulfite converted RNA.
Advantages and Features
- High sensitivty and efficiency - By using an innovative method that enables adaptor tagging of bisulfite-converted RNA to be intact through random probing with blocking formation of un-tagged or half-tagged RNA fragments, both non-barcoded (singleplexed) and barcoded (multiplexed) library preparation can be reliably made with high sensitivity and efficiency, thereby providing a robust and reliable means to build 5mC RNA-seq library. The optimized RNA bisulfite method and enhanced adaptor tagging eliminates loss of fragments and selection bias, which enables input RNA to be as low as 5 ng with increased efficiency of completely tagged cDNA library.
- The entire procedure can be finished in 6 hours. Gel-free size selection/purification saves time and prevents handling errors, as well as loss of valuable samples.
- The innovative reagent composition converts unmethylated cytosine into uracil at a level greater than 99.9%, with no or negligible inappropriate/error conversion of methylcytosine to thymine (<0.1%) when the indicated range of sample RNA is used.
- The kit contains all the required components for each step of the RNA library preparation process, which is sufficient for bisulfite conversion, ligation, clean-up, size selection, and library amplification, thereby allowing the bisulfite RNA library preparation to be streamlined for the most reliable and consistent results.
- Ultra HiFi amplification enables achievement of reproducibly high yields of bisulfite converted RNA libraries with minimal sequence bias and low error rates.
- Starting materials can be total RNA isolated from various tissue/cell samples such as fresh and frozen tissue, cultured cells from a flask or microplate
Background Information
5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in DNA occurs by the covalent addition of a methyl group at the 5-carbon of the cytosine ring by DNA methyltransferases. This process has been well studied and is generally associated with repression of gene expression. It was also observed that in humans, 5-mC occurs in various RNA molecules including tRNAs, rRNAs, mRNAs and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs).
At least 10,275 5-mC candidate sites were discovered in mRNAs and ncRNAs, which cover 10.6% of the total cytosine residues in the transcriptome. 5-mC seems to be enriched in some classes of ncRNA, but relatively depleted in mRNAs. However, the majority (83%) of their candidate sites were found in mRNAs. Within these transcripts 5-mC appears to be depleted within protein coding sequences, but enriched in 5’ and 3’ UTRs.
Two different methyltransferases, NSUN2 and Dnmt2 are known to catalyze 5-mC modification in eukaryotic RNA. Recent data strongly suggest that RNA cytosine methylation affects the regulation of various biological processes such as RNA stability and mRNA translation.
Furthermore, loss of 5-mC in vault RNAs causes aberrant processing into Argonaute-associated small RNA fragments that can function as microRNAs. Thus, impaired processing of vault ncRNA may contribute to the etiology of human disorders related to NSun2-defciency.
Principle & Procedure
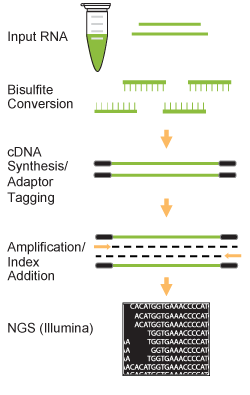
This kit includes all reagents required for a successful RNA bisulfite conversion and bisulfite RNA library preparation using bisulfite-converted RNA generated from a wide range of input RNA amounts (5 ng to 500 ng). In this preparation, RNA is simultaneously bisulfite converted and fragmented to the appropriate length during the bisulfite process.
The bisulfite-treated RNA, which is in single stranded form, is then simultaneously converted to double stranded cDNA and adaptor tagged. The tagged fragments are size selected and purified using MQ binding beads, followed by amplification with a high-fidelity PCR Mix, which ensures maximum yields from minimum amounts of starting material and provides highly accurate amplification of library cDNA with low error rates and minimum bias.
Starting Materials
Starting materials can be total RNA isolated from various tissue/cell samples such as fresh and frozen tissues, cultured cells from a flask or microplate, microdissection samples, and body fluid samples, etc.
The amount of RNA for each bisulfite reaction can be 5 ng to 500 ng. For an optimal reaction, the input RNA amount should be 100 ng to 200 ng.
The yield of RNA purified after bisulfite conversion depends on the amount of input RNA, nature of RNA, and source of the starting material.
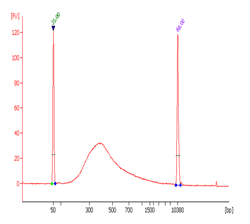
Fig. 2. Size distribution of library fragments: Post-bisulfite cDNA library was prepared from 50 ng of input mouse RNA using the EpiNext™ 5-mC RNA Bisulfite-Seq Easy Kit (Illumina).

