ExoGlow-Vivo EV Labeling Kit (Near IR)
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Product Category: | Exosome Labeling |
Product Description
Monitor in vivo trafficking of EVs with the ExoGlow-Vivo EV Labeling Kit (Near IR), a unique dye developed for following EVs in animal models and tissues. The quick and easy-to-use reagent enables studies critical for the development of EVs as therapeutic agents. Compare how different EV isolation methods affect biodistribution and other in vivo parameters critical for evaluating EV performance
- From EV isolation to injection-ready labeled EVs in less than 1 hour
- Usable with as little as 250 µg of EVs
Performance Data
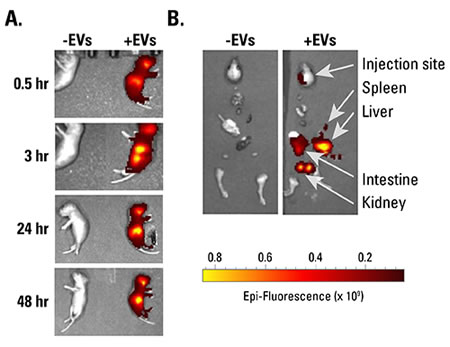
Figure 1. ExoGlow-Vivo labeled EVs show robust signal in vivo. A. HEK293-derived EVs isolated using ExoQuick-TC were labeled with the ExoGlow-Vivo dye and administered intravenously via the superficial temporal vein into post-natal day-4 C57BL6 mice. Animals were imaged at various time points using IVIS® In Vivo Imaging System (PerkinElmer). B. Dissection after 24-hours shows the preferential accumulation of labeled EVs in the liver and kidneys. Data courtesy of Gareth Willis, PhD., Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital.
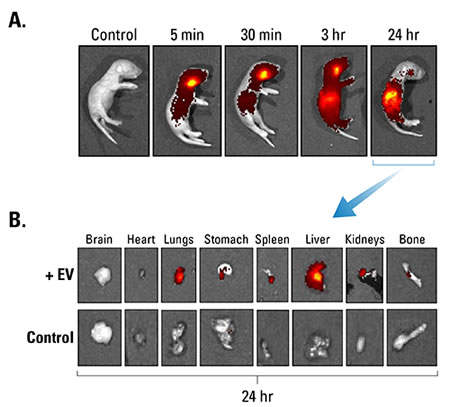
Figure 2. ExoGlow-Vivo dye delivers minimal background. A. Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived EVs were labeled with ExoGlow-Vivo dye and unbound dye removed via ultracentrifugation and a wash. EVs were administered intravenously via the superficial temporal vein into post-natal day-4 FVB mice. Animals were imaged at various time points using an IVIS® In Vivo Imaging System (PerkinElmer). Control refers to supernatant from wash step (i.e. free dye). B. Dissection after 24-hours shows the preferential accumulation of labeled EVs in specific organs and very low residual background signal from free dye. Data courtesy of Gareth Willis, PhD., Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital.
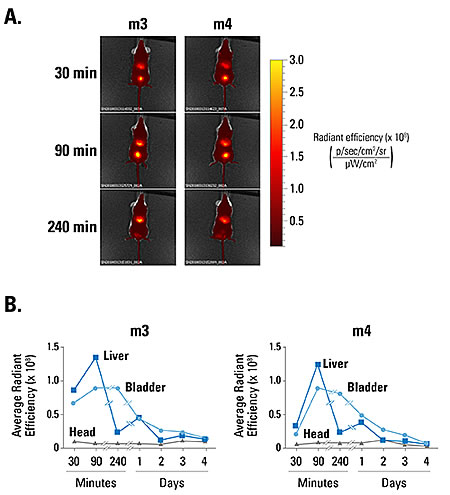
Figure 3. ExoGlow-Vivo enables kinetic analysis of EV persistence in living mice. A. Human PBMC-derived EVs were labeled with ExoGlow-Vivo and administered via tail vein injection into SCID mice (m3 and m4). Animals were imaged at various time points using an IVIS® In Vivo Imaging System (PerkinElmer). B. Plotting signal intensity in different organs (liver, bladder, head) as a function of time after injection shows that EVs are rapidly taken up by target organs within 90-minutes of injection and decline at different rates over time. Data courtesy of Sam Noppen, Rega Institute KU Leuven, Belgium.
- Catalog Number
EXOGV900A-1-SBI - Supplier
SBI System Biosciences - Size
- Shipping
Blue Ice

