StemTAG™ Alkaline Phosphatase Staining Kit (Red)
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Product Category: | Stem Cell Characterization |
Product Description
- Monitor cell differentiation by immunocytochemistry staining of active alkaline phosphatase (AP)
- Staining protocol takes less than 1 hour
- Suitable for human embryonic stem (ES) cells, embryonic germ (EG) cells, and embryonic carcinoma (EC) cells, as well as mouse ES and EG cells
Embryonic stem (ES) cells are continuous proliferating stem cell lines of embryonic origin first isolated from the inner cell mass (ICM). Two distinguishing features of ES cells are their ability to be maintained indefinitely in an undifferentiated state and their potential to develop into any cell within the body.
Based on previous methods developed for mouse ES cells, human ES cell lines were first established by Dr. James Thomson and colleagues. Like mouse ES cells, human ES cells express high levels of membrane alkaline phosphatase (AP) and Oct-4, a transcriptional factor critical to ICM and germline formation. However, unlike mouse ES cells, hES cells do not express stage-specific embryonic antigen (SSEA-1).
Although stem cells from different origins require different growth conditions for self-renewal and display different cell surface markers, AP is the most widely used stem cell marker.
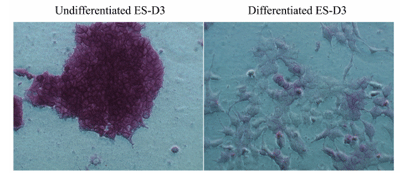
AP staining of ES Cells. Murine embryonic stem cells (ES-D3) are maintained in an undifferentiated stage on gelatin-coated dishes in the presence of LIF, as indicated by the high AP activity. To induce differentiation, LIF was withdrawn over a period of several days; various differentiation events were observed (cells became flattened and enlarged with reduced proliferation). At the end of day 5, AP staining of differentiated cells was performed as described in the Assay Protocol.
The StemTAG™ Alkaline Phosphatase Staining Kit provides an efficient system for monitoring the ES cell undifferentiation/differentiation through immunocytochemistry staining of active AP.
Product Citations
- Vitali, M., S. et al. (2017) Use of the spectrophotometric color method for the determination of the age of skin lesions on the pig carcass and its relationship with gene expression and histological and histochemical parameters. J Anim. doi:10.2
- Lee, K. H. et al. (2016) In vitro ectopic behavior of porcine spermatogonial germ cells and testicular somatic cells. Cell ReprogrAm doi:10.1089/cell.2015.0070.
- Jacinto, F. V. et al. (2015) The nucleoporin Nup153 regulates embryonic stem cell pluripotency through gene silencing. Genes Dev. 29:1224-1238.
- Langlois, T. et al. (2014) TET2 deficiency inhibits mesoderm and hematopoietic differentiation in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 32:2084-2097.
- Lee, K. H. et al. (2014) Identification and in vitro derivation of spermatogonia in beagle testis. PLoS One. . 9:e109963.
- Catalog Number
CBA-300-CB - Supplier
Cell Biolabs - Size
- Shipping
RT

