BirA Biotin Protein Ligase Kit (300.000 units)
Product Description
Biotin-protein ligase (EC 6.3.4.15) activates biotin to form biotinyl 5' adenylate and transfers the biotin to biotin-accepting proteins. It also functions as a biotin operon repressor. The protein is encoded by the birA gene. Other names for this enzyme include: biotin ligase; biotin operon repressor protein; birA; biotin holoenzyme synthetase; biotin-[acetyl-CoA carboxylase] synthetase.
Components provided
- Biomix-A (10X concentration: 0.5 M bicine buffer, pH 8.3)
- Biomix-B (10X concentration: 100 mM ATP, 100 mM MgOAc, 500 µM d-biotin)
- BirA enzyme
- Additional d-biotin
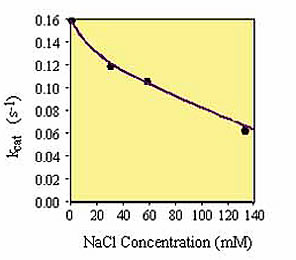
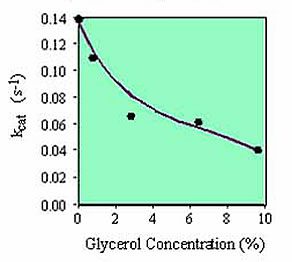
It should be noted that various reagents commonly present in biological buffers can inhibit the activity of birA enzyme including NaCl (100 mM), glycerol (5%) and ammonium sulfate (50 mM). Consequently, the concentration of these reagents in the substrate solution should be minimized. We recommend that, if possible, the substrate should be added to the reaction mix in 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.
BirA Activity as a function of Salt Concentration
BirA Activity as a function of Glycerol Concentration
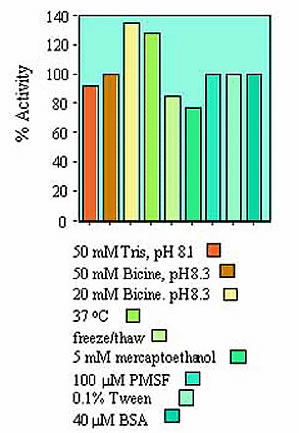
BirA Activity as a function of various Conditions
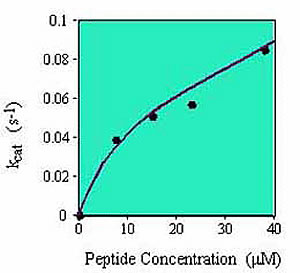
To ensure a rapid rate of biotinylation, it is recommended that the substrate be as concentrated as possible in the final reaction mix (up to 40 µM). The lower the substrate concentration in the reaction mix, the longer it will take to biotinylate. For example, whereas a substrate at 40 µM may be biotinylated in ~30 min., at 4 µM it will take ~5 hrs using the same amount of birA enzyme. To perform the biotinylation in 30 min. (i.e. 10 times faster), it is necessary to add 10 times more enzyme to the reaction mix.
BirA Activity as a function of Peptide Concentration
- Catalog Number
BI001-GC - Supplier
GeneCopoeia - Size
- Shipping
Dry Ice

