Small RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (Indexes 25-48)
Product Description
- Optimized for low input RNA, especially from bodily fluids such as plasma or serum at 1ng of RNA
- Simple and quick workflow: library could be prepared in less than 5 hours
- No gel purification for selected types of samples
- Protocol optimized for RNA isolated from different types of input, including liquid biopsies (blood, plasma, serum and urine)
The Small RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina developed by Norgen is optimized for the generation of small RNA-seq libraries from bodily fluids.
It comprises all the reagents and components required to generate small RNA libraries to be used for next generation sequencing on an Illumina platform. A purification module is also provided for rapid purification of nucleic acid products generated at various steps of the workflow.
The purification module utilizes Norgen’s patented resin technology which enhances recovery of desired library intermediates or final products. The library prep workflow could be used for different forms of input including purified total RNA or enriched small RNA, as well as RNA from low content inputs such as plasma, serum and urine. To improve sequencing results when analyzing serum samples, the Norgen Abundant Sequence Depletion Kit (Cat# 63440-NB / 63540-NB) can be used to specifically remove an abundant RNA in human plasma/serum that usually takes up > 50% reads of a standard small RNA-Seq run.
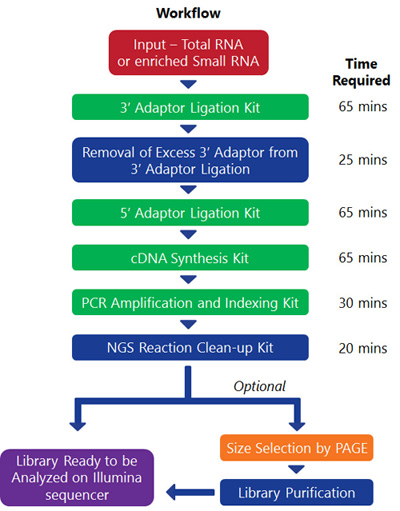
How it works
Performance Data
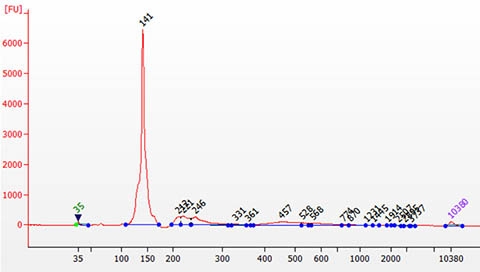
Figure 1. An example of a purified small RNA library on an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer using a High Sensitivity DNA Chip. The library was prepared using a mixture of synthetic microRNAs as an input. A single peak of ~ 141 bp was obtained and could be used directly for analysis on an Illumina next-generation sequencing platform

Figure 2. An example of a small RNA library on resolved on a 6% Novex® TBE PAGE gel. The library containing microRNAs resolved at around 140 bp and migrated just below the 150 bp marker of the provided NGS MW Ladder. The NGS Control Ladder contains two bands for alignment during band excision. The top band co-migrate with the expected size of library construct containing mainly microRNAs (~140 bp). The bottom band co-migrate with the expected size of an adaptor-adaptor-ligation product (~ 120 bp) that should be excluded.
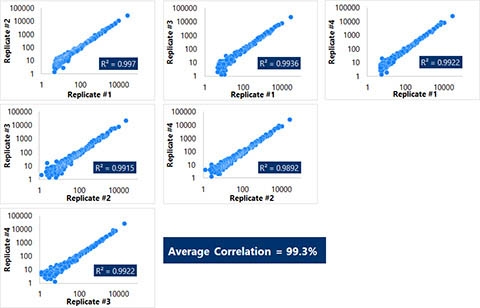
Figure 3. Superb reproducibility of constructing small RNA (microRNA) sequencing libraries from liquid biopsies samples with low RNA abundance. Total RNA was prepared from 200 µL of EDTA-plasma using Norgen's Plasma/Serum RNA Purification Mini Kit (Cat# 55000-NB). Small RNA libraries (four replicates) were prepared from purified RNA using Norgens Small RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (Cat# 63600-NB) without the use of gel purification (prep time of ~ 5 hours). The resulting libraries were sequenced on Illumina's MiSeq system using v3 chemistry. Reads were mapped to microRNAs and normalized to reads per million. Pairwise-comparisons of microRNA expression among all replicates were performed. High correlations (or reproducibility) were observed among all replicates with an average of over 99%.
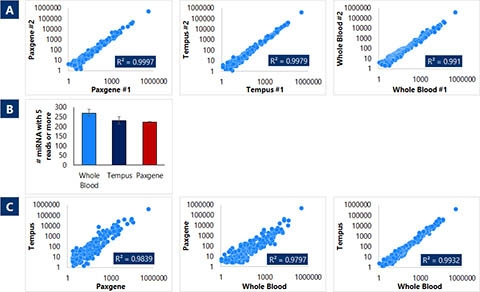
Figure 4. Combining true total RNA purification technology with robust production of small RNA (microRNA) sequencing libraries from RNA purified from whole blood and preserved blood. Total RNA was prepared from either whole blood or collected in Paxgene™ or Tempus™ blood tubes using Norgens Total RNA Purification Plus Kit (Cat# 48300-NB), Preserved Blood RNA Purification Kit II (for use with Paxgene™ Blood RNA Tubes) (Cat# 43500-NB) or Preserved Blood RNA Purification Kit I (for use with Tempus™ Blood RNA Tubes) (Cat# 43400-NB), respectively, in duplicates. Small RNA libraries were prepared from purified RNA using Norgen's Small RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (Cat# 63600-NB). The resulting libraries were sequenced on Illumina's MiSeq system using v3 chemistry. Reads were mapped to microRNAs and normalized to reads per million. Pairwise-comparisons of microRNA expression among all replicates were performed. High correlations (or reproducibility) were observed among all replicates of each blood tube with an average of over 99% (Panel A). Moreover, all three types of blood samples yielded similar numbers of microRNA detected (Panel B) with highly correlated expression profiles (Panel C).
Product Citations
- Li, J., Kho, A., Tiwari, A., Chase, R., Weiss, S. T., Hobbs, B. D., McGeachie, M., & Tantisira, K. G. (2020) Connecting Past with Future - Circulating Micrornas Can Mediate Asthma Exacerbations in the Childhood Asthma Management Program (CAMP)
- Li, J., Panganiban, R., Kho, A. T., McGeachie, M. J., Farnam, L., Chase, R. P., Weiss, S. T., Lu, Q., & Tantisira, K. G. (2020) Circulating MicroRNAs and Treatment Response in Childhood Asthma American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
- Catalog Number
63620-NB - Supplier
Norgen Biotek - Size
- Shipping
Dry Ice

