H3K27me3 Antibody, SNAP-Certified™ for CUT&RUN and CUT&Tag
Product Description
This H3K27me3 (histone H3 lysine 27 trimethyl) antibody meets EpiCypher's lot-specific SNAP-Certified™ criteria for specificity and efficient target enrichment in both CUT&RUN and CUT&Tag applications. This requires <20% cross-reactivity to related histone PTMs determined using the SNAP-CUTANA™ K-AcylStat Panel of spike-in controls. High target efficiency is confirmed by consistent genomic enrichment at varying cell inputs: 500k and 50k cells in CUT&RUN; 100k and 10k cells in CUT&Tag. High efficiency antibodies display similar peak structures at representative loci and highly conserved genome-wide signal even at reduced cell numbers. H3K27me3 is associated with repressed genes [1] and is anti-correlated with H3K4me3, a marker of active gene transcription enriched at transcription start sites.
Validation Data - CUT & Tag
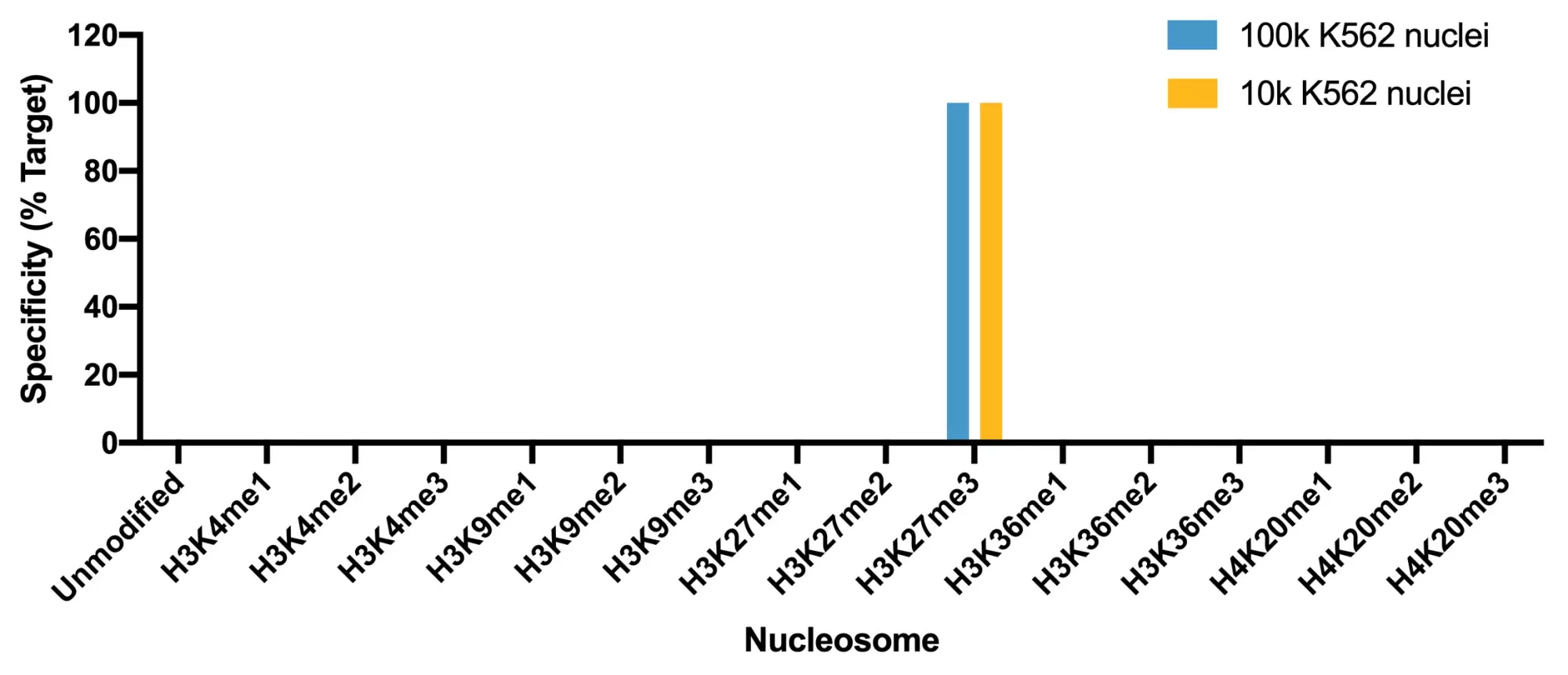
Figure 1: SNAP specificity analysis in CUT&Tag. CUT&Tag was performed aand CUT&Tag sequencing reads were aligned to the unique DNA barcodes corresponding to each nucleosome in the K-MetStat panel (x-axis). Data are expressed as a percent relative to on-target recovery (H3K27me3 set to 100%).
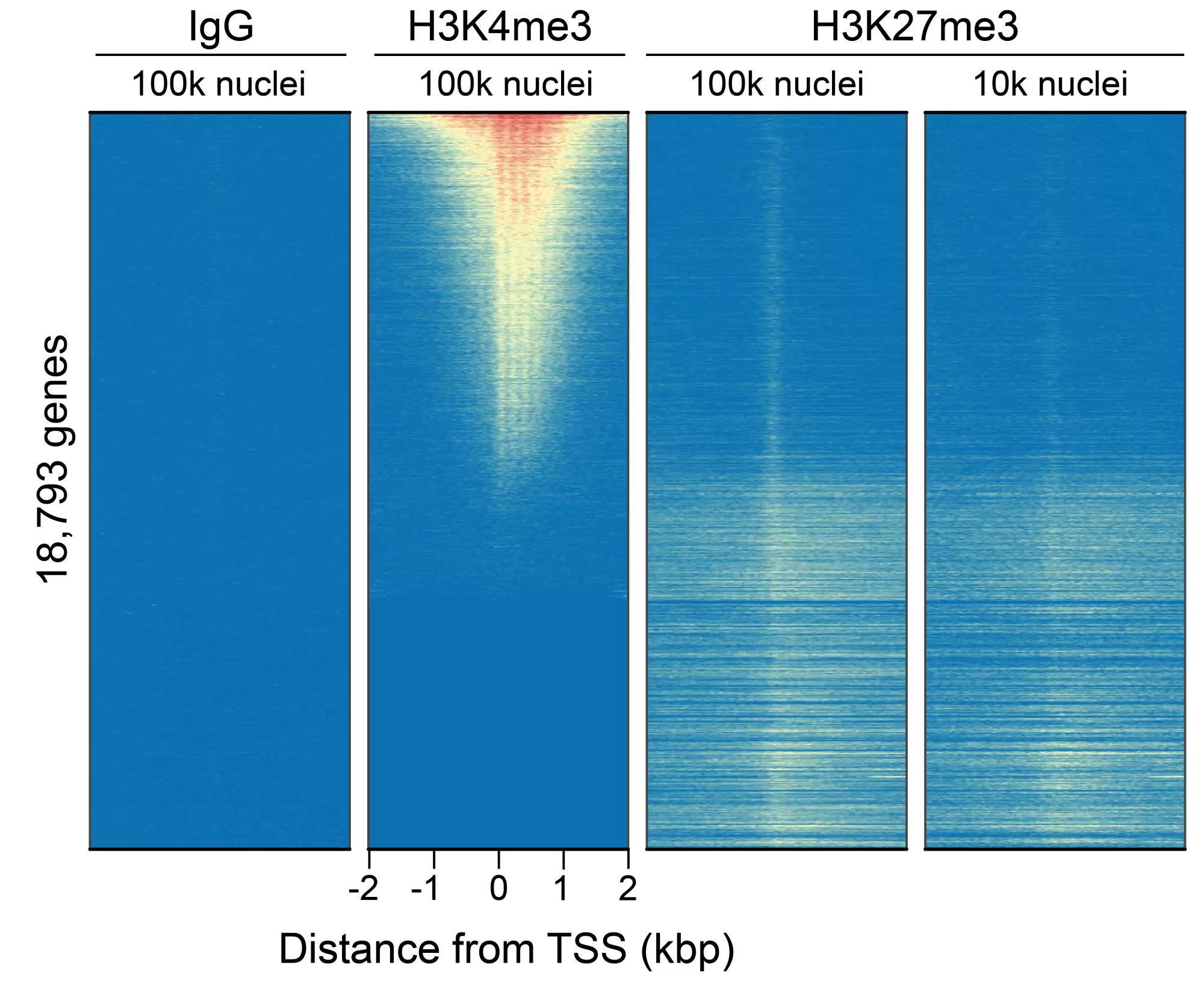
Figure 2: CUT&Tag genome-wide enrichment. CUT&Tag was performed and sequence reads were aligned to 18,793 annotated transcription start sites (TSSs ± 2 kbp). Signal enrichment was sorted from highest to lowest (top to bottom) relative to the H3K4me3 - 100k nuclei sample (all gene rows aligned). High, medium, and low intensity are shown in red, yellow, and blue, respectively. H3K4me3 positive control and H3K27me3 antibodies produced the expected diametric enrichment pattern, which was consistent between 100k and 10k nuclei and greater than the IgG negative control.
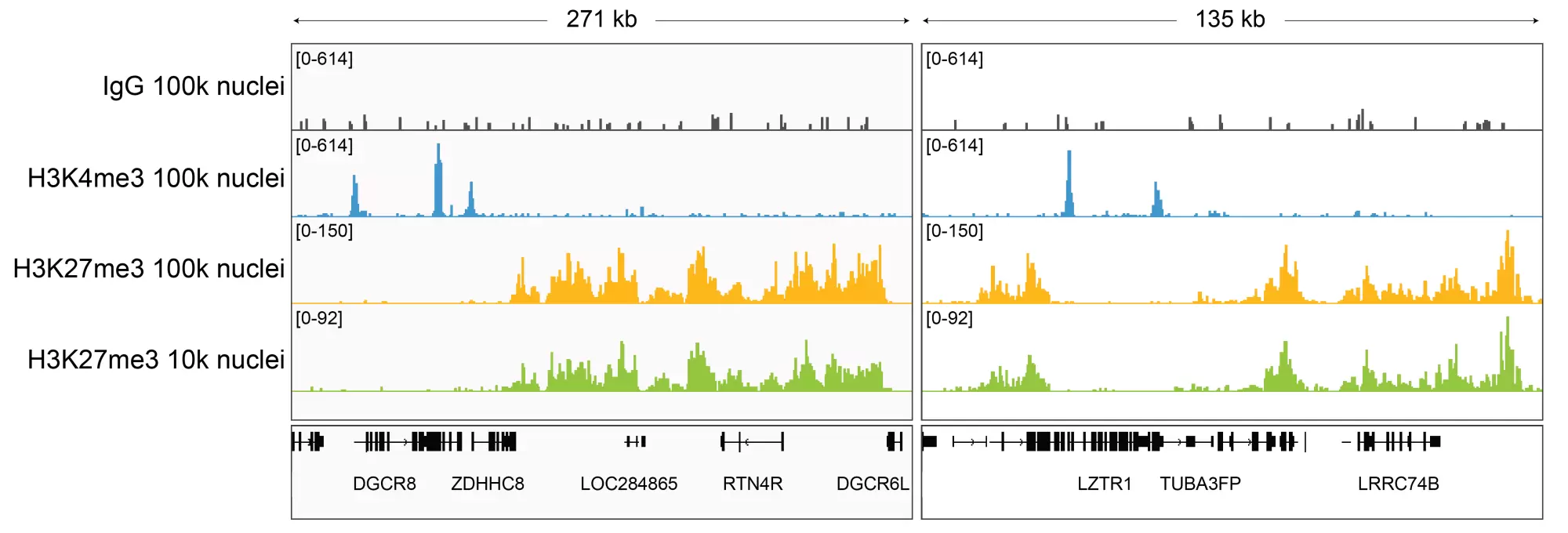
Figure 3: H3K27me3 CUT&Tag representative browser tracks. CUT&Tag was performed and gene browser shots were generated using the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV, Broad Institute). H3K27me3 antibody tracks display the characteristic broad, intergenic enrichment known to be consistent with the function of this PTM. Similar results in peak structure and location were observed for both 100k and 10k nuclei inputs.
Validation Data - CUT & RUN
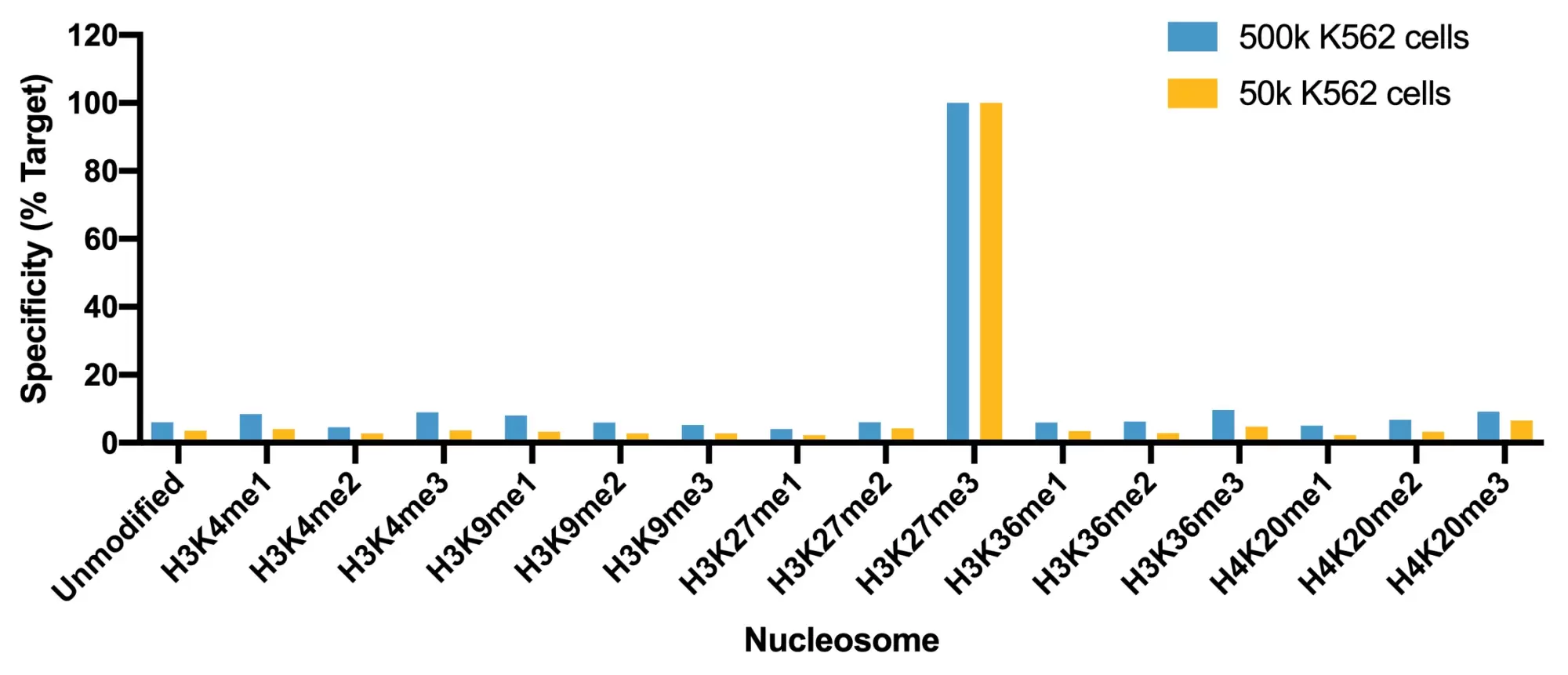
Figure 4: SNAP specificity analysis in CUT&RUN. CUT&RUN was performed and CUT&RUN sequencing reads were aligned to the unique DNA barcodes corresponding to each nucleosome in the K-MetStat panel (x-axis). Data are expressed as a percent relative to on-target recovery (H3K27me3 set to 100%).
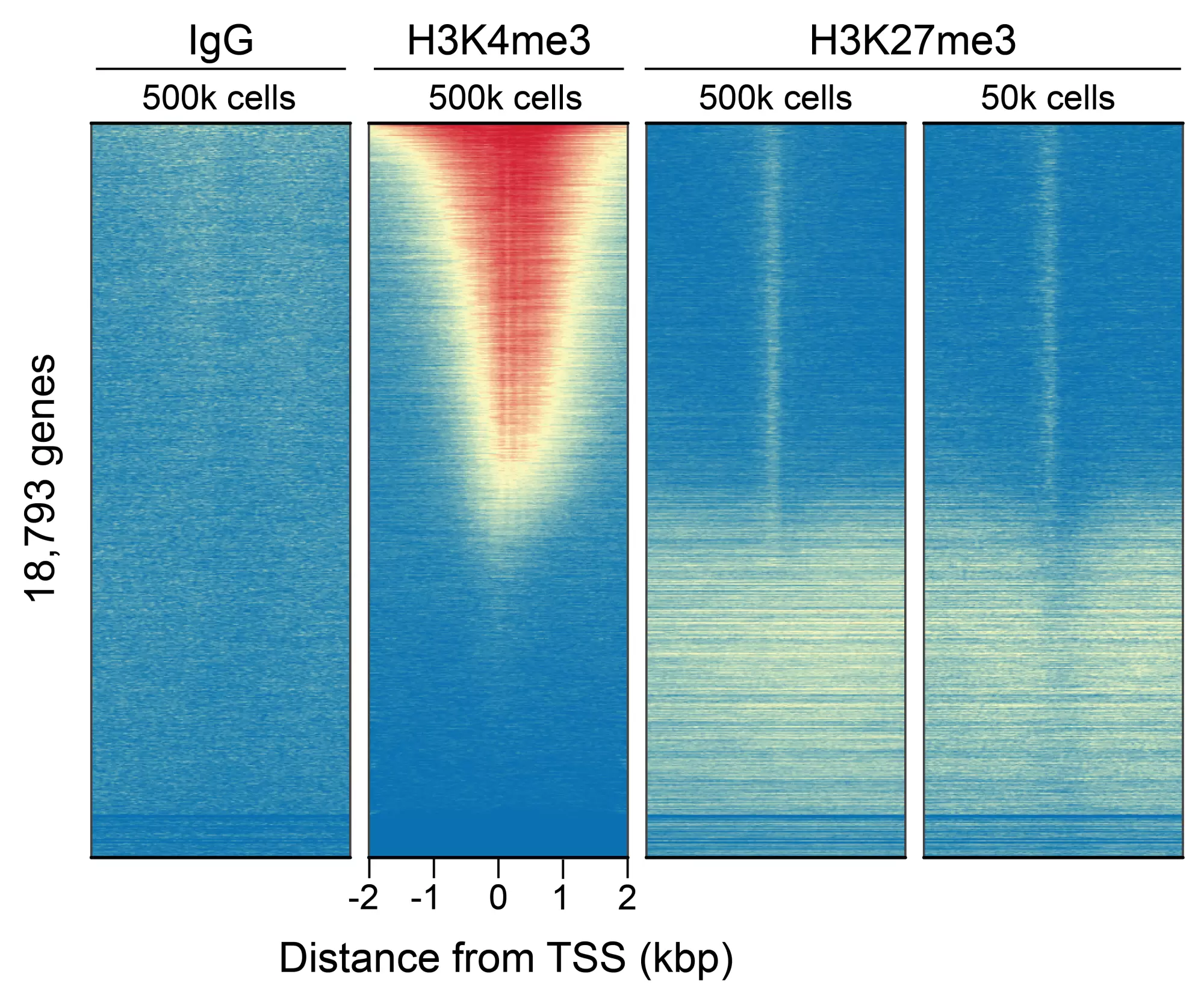
Figure 5: CUT&RUN genome-wide enrichment. CUT&RUN was performed and sequence reads were aligned to 18,793 annotated transcription start sites (TSSs ± 2 kbp). Signal enrichment was sorted from highest to lowest (top to bottom) relative to the H3K4me3 - 500k cells sample (all gene rows aligned). High, medium, and low intensity are shown in red, yellow, and blue, respectively. H3K4me3 positive control and H3K27me3 antibodies produced the expected diametric enrichment pattern, which was consistent between 500k and 50k cells and greater than the IgG negative control.

Figure 6: H3K27me3 CUT&RUN representative browser tracks. CUT&RUN was performed and gene browser shots were generated using the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV, Broad Institute). H3K27me3 antibody tracks display the characteristic broad, intergenic enrichment known to be consistent with the function of this PTM. Similar results in peak structure and location were observed for both 500k and 50k cell inputs.
Background References
[1] Cai et al. Nature Communications (2021). PMID: 33514712
Product Citations
- Lucie Darmusey, Anna J Bagley, Thai T Nguyen, Hanqian L Carlson, Hunter Blaylock, Shawn B Shrestha, Amara Pang, Samantha Tauchmann, Sarah C Taylor, Amy C Foley, Katia E Niño, Eric M Pietras, Theodore P Braun, Julia E Maxson (2025) Dual ASXL1 and CSF3R mutations drive myeloid biased stem cell expansion and enhance neutrophil differentiation. Blood advances
- Segert Julian A., Bulyk Martha L. (2025) Histone H4 lysine 20 monomethylation is not a mark of transcriptional silencers bioRxiv
- Turano Paolo S., Akbulut Elizabeth, Dewald Hannah K., Vasilopoulos Themistoklis, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly Patricia, Herbig Utz, MartÃnez-Zamudio Ricardo Iván (2025) Epigenetic mechanisms regulating CD8+ T cell senescence in aging humans bioRxiv
- Arun Padmanabhan, Yvanka de Soysa, Angelo Pelonero, Valerie Sapp, Parisha P. Shah, Qiaohong Wang, Li Li, Clara Youngna Lee, Nandhini Sadagopan, Tomohiro Nishino, Lin Ye, Rachel Yang, Ashley Karnay, Andrey Poleshko, Nikhita Bolar, Ricardo Linares-Saldana, Sanjeev S. Ranade, Michael Alexanian, Sarah U. Morton, Mohit Jain, Saptarsi M. Haldar, Deepak Srivastava, Rajan Jain (2024) A Genome-Wide CRISPR Screen Identifies BRD4 as a Regulator of Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Nature cardiovascular research
- Campbell Elyssa M., Laven-Law Geraldine, Smith Grady, Peters Timothy J, Colino-Sanguino Yolanda, Moulder David, Du Qian, Jones Alicia, Giles Katherine A., Khoury Amanda, Stirzaker Clare, Hickey Theresa A., Mora Fatima Valdes, Clark Susan J., Achinger-Kawecka Joanna (2024) Androgen stimulation rapidly reorganizes temporal 3D genome and epigenome states to trigger AR-mediated transcription in prostate cancer bioRxiv
- Catalog Number
13-0055-EPC - Supplier
EpiCypher - Size
- Shipping
Blue Ice

