DNA-seq Following Genetic Screens
NGS of CRISPR, RNAi and Barcode Libraries
Primers and reagents to prepare sgRNA, shRNA or barcodes from pooled lentiviral library screens for sequencing
Screens using complex pooled CRISPR and RNAi libraries make use of next generation sequencing read counts to assess the relative representation of each library element in the genomic DNA of the screened cell or tissue sample. Preparation of these short specific library elements - shRNA, sgRNA or barcodes - for sequencing requires targeted PCR amplification with specially designed primers followed by sequencing with customized primers.
- Amplify and sequence shRNA, sgRNA or barcodes from genomic DNA samples
- Get enumerated shRNA, sgRNA or barcode counts for downstream analysis
- Use a complete NGS preparation kit with all reagents and primers needed
Multiplex analysis of multiple samples requires more than 15 primers customized based on the design of each particular library. For most of the standard pooled lentiviral libraries, including Cellecta, GeCKO and Brunello, BioCat offers complete kits containing all the primers and PCR reagents required to prepare genomic DNA isolated from your library screening samples for sequencing.
- NGS Preparation Kits for sgRNA Libraries
- NGS Preparation Kits for shRNA Libraries
- NGS Preparation Kits for Barcode Libraries
Alternatively, we provide complete NGS and analysis services for researchers running their own screens with pooled libraries.
Applications
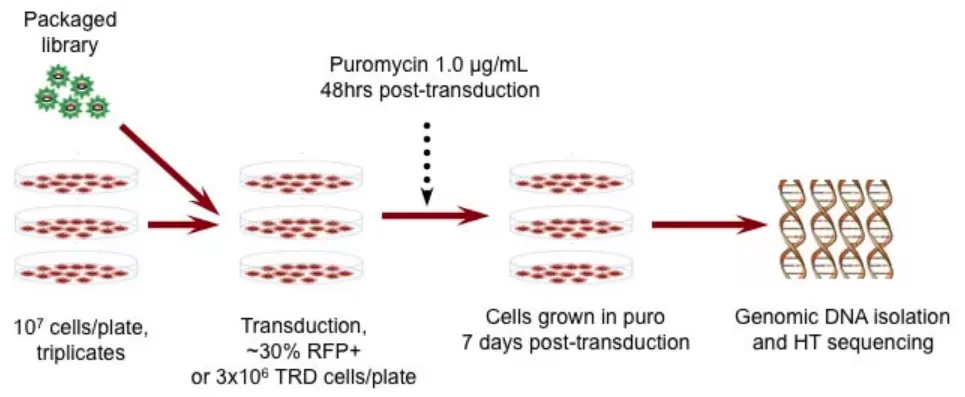
After running screens with pooled lentiviral CRISPR, shRNA, or barcode libraries, genomic DNA from the whole transduced population of cells is isolated, and the frequency of each integrated shRNA, sgRNA, or barcode lentiviral construct in the population is assessed by next generation sequencing (NGS).
For CRISPR and shRNA screens, the frequency of each guide or hairpin is assessed to determine which ones are enriched or depleted relative to the original libraries or control samples. For example, “dropout viability” screens may be run to identify sgRNA or shRNA that are toxic to cells because they target essential genes. This sort of screen is often used to look for genetic susceptibilities in cancer cells.
With barcoding studies, cells labeled by transduction of complex pooled libraries of unique DNA sequences are similarly sequenced to assess the diversity and quantities of each of the barcodes present in the cell population.