microRNA Precursor & Knockdown Constructs
microRNA Precursor & Knockdown Constructs
Alter gene expression or study microRNA function with human and mouse lentivector-delivered precursors that are efficiently and accurately processed into mature microRNAs or permanently knockdown microRNAs with miRZip anti-microRNA Expression Lentivectors and gain a thorough understanding of microRNA function.
Lenti-miR pre-microRNA Expression Constructs
Whether you’re using microRNAs to study cellular processes or develop the next generation of therapeutics, SBI’s comprehensive collection of human and mouse precursor microRNA lentivectors are a superior alternative to synthetic microRNAs. Like synthetic microRNAs, SBI’s human and mouse pre-microRNA expression constructs can be transfected into target cells for transient microRNA expression. But unlike synthetic microRNAs, they can also be transduced into a variety of target cells—including primary cells, stem cells, and other hard-to-transfect cell lines—to create stable microRNA-producing cell lines, maximizing your options for microRNA expression.
Pooled Human Lenti-miR Libraries for efficient microRNA screening as well as Human and Mouse pre-microRNA Scramble Negative Controls are also available.
- Transfect or transduce the precursor microRNA lentivectors
- Create stably-expressing microRNA cell lines
- Obtain accurate microRNA processing and efficient expression through the use of native precursor sequences
- Use copGFP or puromycin marker to identify desired clones
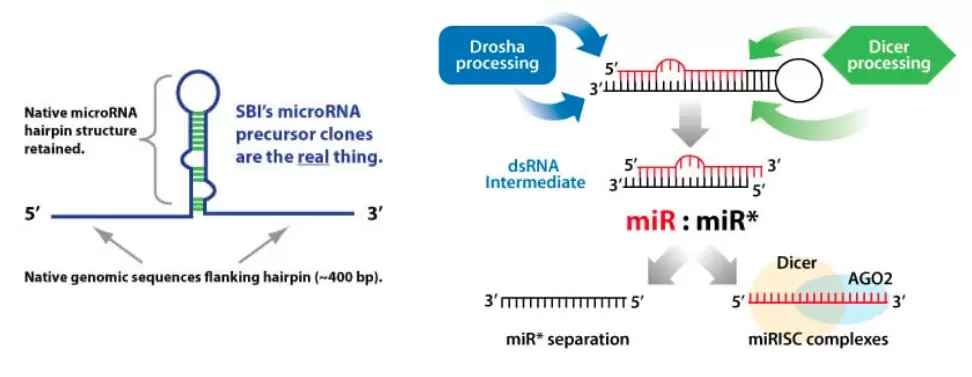
SBI’s Lenti-miRs are designed for efficient expression and accurate processing into mature microRNAs, for native microRNA-like behavior. Each construct is cloned with the native stem-loop structure plus an additional 200–400 bps of upstream and downstream DNA, ensuring that the microRNA processing machinery operates just as it would with the native transcript.
How It Works
Pre-microRNA Expression Lentivectors use the native microRNA processing machinery.
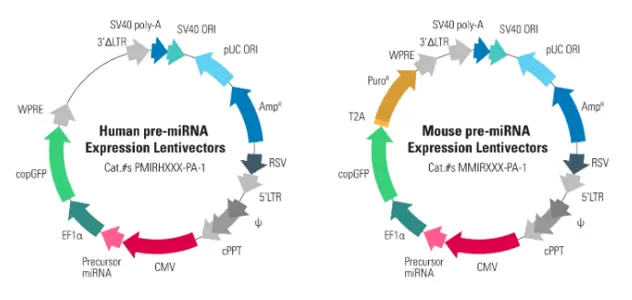
Human & Mouse pre-microRNA Expression Lentivectors
The precursor microRNA expression lentivectors drive expression of the microRNA precursor with the constitutive CMV promoter, for strong expression in common cell types including HeLa, HEK293, and HT1080 cell lines. Transductants/transfectants can be easily selected for or sorted using copGFP or puromycin markers.
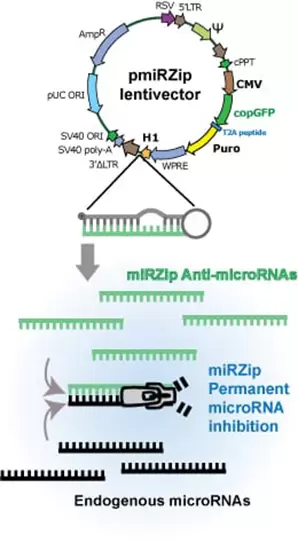
miRZip anti-microRNA Expression Constructs
Leveraging SBI’s powerful and well-regarded third-generation lentivector technology, each of their miRZip lentivectors expresses a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) that, after processing, preferentially produces an anti-sense microRNA. The hairpin is rationally designed to be asymmetric, ensuring that the sense strand does not contain the endogenous microRNA sequence and enabling accumulation of the anti-microRNA. The result is robust derepression of the transcripts targeted by the microRNA being “zipped,” and elevation of the corresponding protein levels.
In addition, a miRZip Pooled anti-microRNA Knockdown Library for high-throughput phenotypic screening as well as a miRZip anti-microRNA Scramble Negative Control are offered.
- Stable and permanent anti-microRNA expression from a constitutive H1 promoter
- Rationally designed, asymmetric hairpins optimized for anti-sense microRNA production
- Efficient suppression of specific endogenous microRNAs
- Reliable delivery to dividing or non-dividing cells
- Selection/sorting for transfected/transduced cells with either copGFP or puromycin
How It Works
miRZip shRNAs produce short, single-stranded anti-microRNAs that competitively bind their endogenous microRNA target and inhibit its function.