DriverMap Targeted Expression Profiling
DriverMap Targeted Expression Profiling (EXP)
Genome-wide, targeted expression analysis that combines the sensitivity of multiplex PCR with the dynamic range and throughput of NGS
- Single-tube, one-day protocol starting with as little as 10 ng total RNA to NGS library for sequencing with next-generation sequencing (NGS) readout
- Higher sensitivity for low expressed genes than RNA-Seq with 10-fold less sequencing depth required
- Simplified analysis against reference sequences - genomic alignment not needed
The DriverMap Targeted Expression Profiling Platform enables targeted multiplex PCR amplification and next-generation profiling to measure the expression levels of up to 19,000 human protein-coding genes in a single assay. By combining highly multiplexed RT-PCR amplification with the depth and precision of next-generation sequencing (NGS) quantitation, the DriverMap assay provides convenient, comprehensive, highly sensitive, and quantitative measurement of gene expression.
Available off-the-shelf assay formats include the DriverMap EXP Human Genome-Wide 19K Profiling Kit, V3 and a number of panels of expertly curated gene targets, see table below.
A DriverMap Targeted RNA Sequencing Service can be offered as well.
How It Works
Rather than reverse-transcribing the whole transcriptome, the DriverMap assay combines multiplex RT-PCR amplification to amplify defined and conserved 80- to 200- base regions of the targeted genes, and then uses next-generation sequencing (NGS) to quantitatively assess abundance levels of each of these transcript amplicons.
There are significant advantages to targeting, amplifying, and sequencing carefully selected discrete loci of interest in the expressed transcriptome. Gene-specific primers that target each gene of interest obviate the need for RNA preparation to remove unwanted sequences such as ribosomal RNA, beta-globins, or other non-coding RNA. Only transcript sequences matching the targets of interest are amplified. Therefore, only a small amount of total RNA is needed for this highly sensitive assay. As little as 10 pg of total RNA from single-cell lysate is enough to detect most target transcripts.
Also, the NGS read depth required to reliably read several thousand targeted amplicons is much less than the depth required for the whole transcriptome. As a result, the targeted approach detects lower-abundance expressed transcripts more consistently and reliably than other RNA-seq approaches and much less sequencing depth is required.
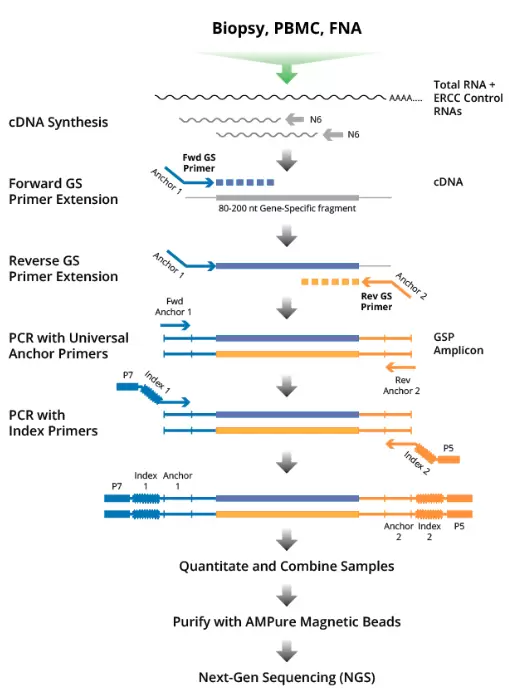
Analysis of the sequencing results is much simpler with the DriverMap targeted approach since each amplicon corresponds to a known reference sequence. There is no need to estimate gene copy number from assembled cDNA fragments. With targeted RT-PCR the read levels of each amplicon directly correlate to the expression levels of the target transcript. The analysis can be done entirely on an Excel spreadsheet using housekeeping genes as references in a manner similar to standard qRT-PCR. Software is included with the DriverMap kit to enable this amplicon alignment and to generate a spreadsheet of read counts for targets directly from the Illumina FASTQ file.
Please note: The DriverMap EXP Human Genome-Wide 19K Profiling Kit, V3 uses gene-specific primers for first-strand cDNA synthesis resulting in highly reduced background.
DriverMap Assay vs RNA-seq
Compared to RNA-Seq, the DriverMap EXP Solution offers:
- Simple, one-tube protocol that enables processing of 96+ samples a day
- Ability to directly use total RNA or cell lysate for small and single-cell samples
- Improved detection of medium- and low-abundance transcripts with 5-fold less NGS sequencing depth. (Figs 2, 4)
- Broad dynamic range that enables quantitative measurement of 2-3 times more transcripts than RNA-Seq. (Fig 3)
- Straightforward data analysis that can be conveniently done on any laptop using standard spreadsheet software

Figure 2 Comparison of the sensitivity of targeted RNA-Seq (~25 million reads/sample) vs. DriverMap EXP assay (~5 million reads/ sample).
NGS read levels for selected high-abundant (10K-100K copies per sample), medium-abundant (1K to 10K copies per sample), and low-abundant
transcripts (100-1K copies per sample) in 50ng of total RNA from seven common cancer cell lines.

Figure 3 Sensitive and Reproducible. The correlation (R-squared values) of detected genes between human universal RNA and total brain RNA using the DriverMap EXP assay remains highly consistent regardless of sample, across amounts ranging from 10 pg to 50 ng of starting total RNA.
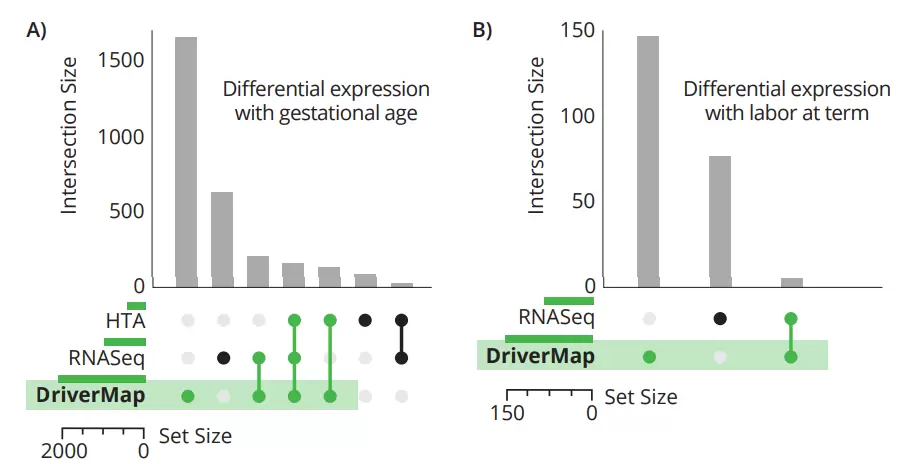
Figure 4 Comparison of three expression profiling methods for biomarker discovery.
• 3x more protein-coding aligned reads with DriverMap than RNA-Seq
• More sample-to-sample consistency than with RNA-Seq
• DriverMap expression results correlated better with qRT-PCR results; Tarca, et al., Scientific Reports 9:848 (2019)
Reference
Tarca AL et al. (2019) Targeted expression profling by RNA-Seq improves detection of cellular dynamics during pregnancy and identifes a role for T cells in term parturition. Scientific Reports 9:848