DriverMap Adaptive Immune Receptor Profiling
DriverMap Adaptive Immune Receptor (AIR) TCR-BCR Profiling
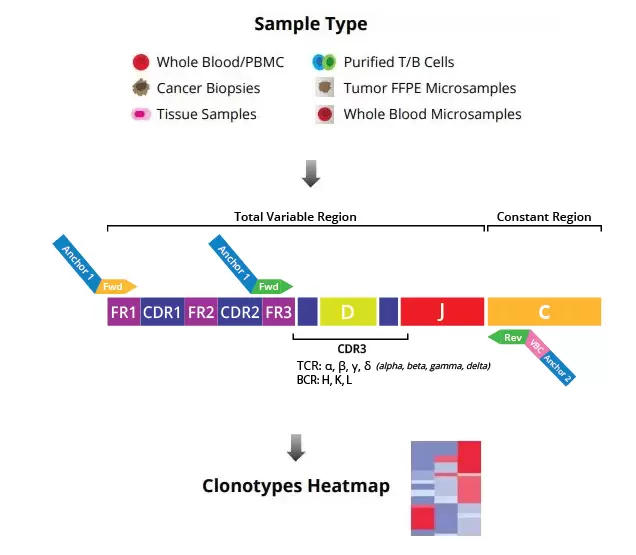
Profile the full-length receptor region or only the CDR3 repertoire of all 7 TCR and BCR chains in a single-tube, single-day assay
DriverMap AIR is the only assay technology on the market that profiles the full-length receptor region or only the CDR3 repertoire of all T-cell receptor (TCR)--TRA, TRB, TRG and TRD--and B-cell receptor (BCR)--IGH, IGK and IKL--chains in an single-tube, single-day assay using multiplex RT-PCR and next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology without the need of any additional specialized equipment. Cellecta offers AIR assays to profile human or mouse RNA, DNA, or both. The simultaneous profiling of DNA and RNA enables the identification of antigen-activated clonotypes to provide even greater insight into the immune response.
The DriverMap AIR-RNA assay quantifies T-cell and B-cell receptor transcripts. Assaying expression of the immune receptors from either the CDR3 OR the full-length receptor region enables highly sensitive detection of low-frequency, rare TCR and BCR clonotypes, and more comprehensive profiling when working with small samples and limited numbers of cells. Fig.3. shows that the DriverMap AIR-RNA assay can detect all seven TCR and BCR chains from a single sample of RNA.
The DriverMap AIR-DNA assay amplifies receptor genes directly from genomic DNA. The AIR-DNA assay provides a more quantitative measurement of the genetic copies for each CDR3-specific clonotype which correlates to the number of cells with that clonotype in the sample. This data enables the measurement of clonal expansion in T and B cells.
Combining data obtained from both the AIR-DNA and AIR-RNA assays enables the assessment of both transcriptional activation and number of cells with a particular clonotype. The ability to differentiate these two effects provides a quantitative basis for detecting antigen-activated clonotypes. For example, it is evident from the data in Fig. 4, that particular TRB clonotypes, even when present in only a small portion of the cells in a population, can be highly up-regulated.
How It Works
- Start from RNA or DNA from a variety of immune sample types such as whole blood, PBMCs, cancer biopsies, tissue samples, FFPE or dried blood microsamples
- Detect and accurately quantify AIR clonotypes with the multiplex PCR-based assay making use of validator barcodes (VBCs)
- Obtain more sensitive and reproducible profiling data
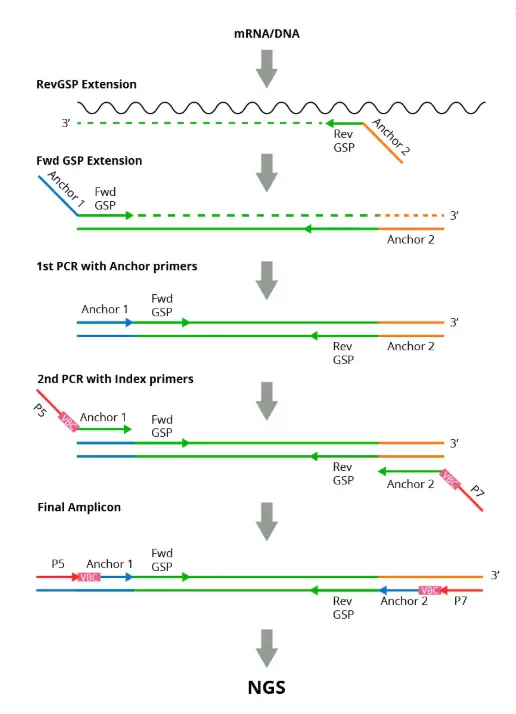
Fig.2. Workflow of RNA/DNA assay.
DriverMap AIR differs from other Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire (AIRR) Assays
- DriverMap™ Multiplex PCR technology uses gene-specific primers which significantly reduce the level of non-specific binding and primer-dimer amplification products, and are designed to target only TCR/BCR isoforms.
- Validator barcodes (VBCs) facilitate accurate quantitation of the copy number of cDNA or DNA molecules in amplification steps, as well as detection of low abundance clonotypes and correction of amplification biases and sequencing errors.
- Dual-index amplicon labeling strategy minimizes index hopping during NGS allowing for comprehensive readouts.
- Full profiles of the antigen-recognition CDR3 region enable assessment of CDR3 length distribution, V(D)J segment usage, isotype composition for BCRs, somatic mutations, and similar characteristics with immune receptor profiling software such as MiXCR (MiLabs).
Applications of BCR Sequencing
- Identify broadly neutralizing antibodies (BNAbs) and map Ig-seq datasets to known antibody structures for antibody and vaccine development
- Track B-cell migration and development patterns
- Find clinical markers of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis and cancers (e.g. B-cell lymphoma)
- Contrast naïve and antigenically challenged datasets for understanding antibody maturation
Applications of TCR Sequencing
- Track T-cell clonality and diversity for mechanism of action of immune checkpoint inhibitors for immunotherapies
- Assess TCR overlap between repertoires to define spatial and temporal heterogeneity of the anti-tumoral immune response
- Analyze TCR sequence and structure to annotate antigenic specificity for developing personalized cellular immunotherapies
Spike-In Controls
To ensure consistent and reproducible T-cell Receptor (TCR) and B-cell Receptor (BCR) clonotype profiling Cellecta designed the DriverMap Adaptive Immune Receptor (AIR) RNA Spike-in Controls. A collection of synthetic mRNA constructs is offered that may be used as universal controls for commercial and home-brewed AIR sequencing assays based on multiplex RT-PCR or 5’-RACE (SMART) PCR techniques.
Supporting Data
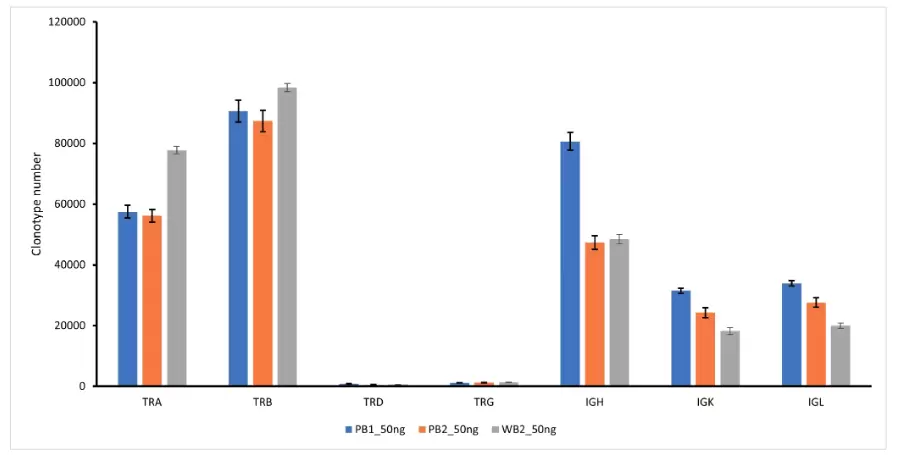
Fig.3. Number of clonotypes for 7 TCR/BCR chains identified in 50ng of normal PBMC or whole blood RNA (10x10^6 reads per sample, triplicates).
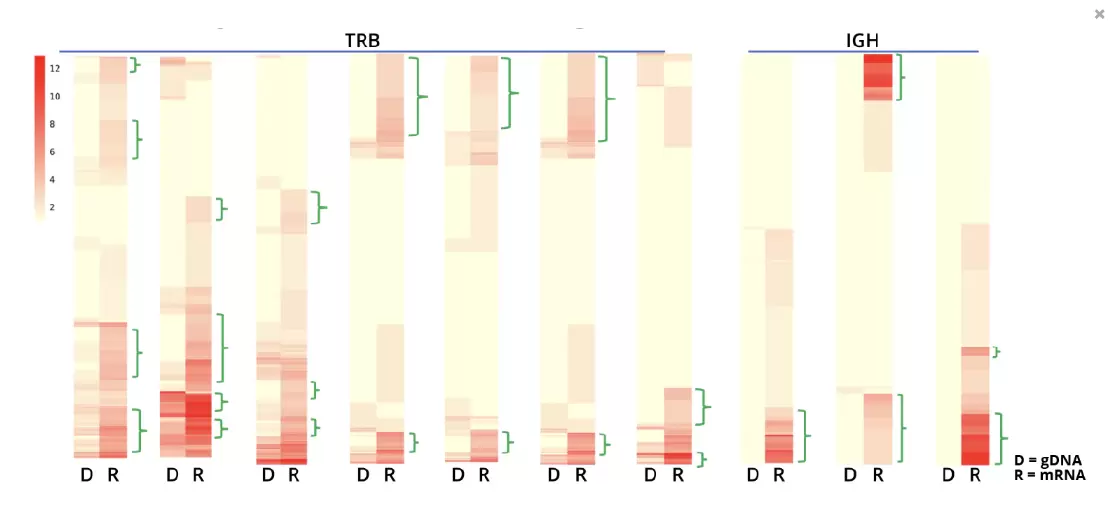
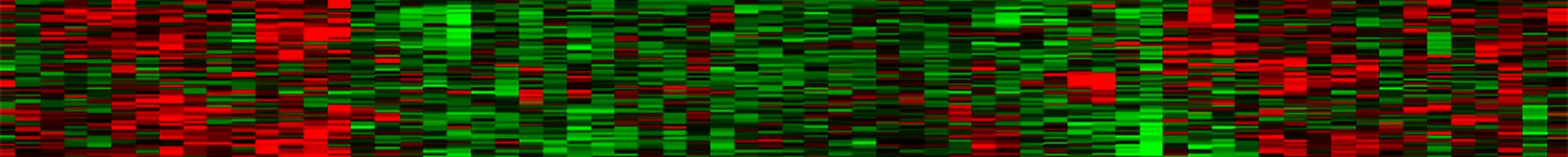
Fig.4. Detection of Cancer-Activated CDR3 Clones. The red intensity of each line in the paired heat maps shows the detection level of each TCR or BCR clonotype in each sample with the DriverMap AIR-RNA (R) and a competitor DNA (D) assay. By comparing the normalized level of clonotype expression as measured by the AIR-RNA assay with the frequency of each clonotype in the population as measured by the DNA-based assay, it is evident that 5-10% of the clones (indicated by green brackets) are strongly up-regulated even when they are only weakly detected at the DNA level, indicating they are not highly represented in the population.
Product Flyers and Other Resources
- Flyer: Comprehensive Adaptive Immune Receptor Profiling for All Immune Sample Types
- Video: Improved Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire Profiling for Biomarker Discovery (23:08)
DriverMap Adaptive Immune Receptor (AIR) TCR-BCR Profiling Service
Do you have immune samples you would like to profile? Provide us with some information on your samples and your study goals, and we will get back to you to discuss your project.